PCB Assembly Manufacturing Process Flow Chart
The process of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) assembly is integral to electronics manufacturing. It involves several stages, from designing the circuit to testing the final product. Understanding this process is crucial for businesses that rely on high-quality PCBs for their products. In this article, we will explore the PCB assembly manufacturing process flow chart, detailing each step in the journey from PCB design to the finished assembly.
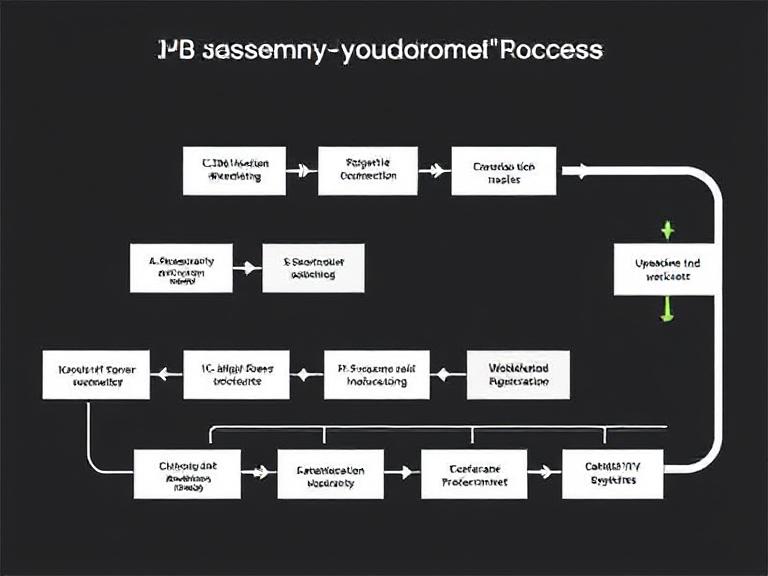
Table of Contents
- What is PCB Assembly?
- PCB Assembly Process Flow
- Stages of the PCB Assembly Process
- Role of Wintech in PCB Assembly
- Key Benefits of PCB Assembly
- Conclusion
What is PCB Assembly?
PCB Assembly (PCBA) refers to the process of soldering electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB). This process involves various steps, including component placement, soldering, testing, and inspection. PCBA is a critical step in the production of electronic devices such as smartphones, computers, and medical equipment.
PCB Assembly Process Flow
The PCB assembly process can be broken down into several key stages. These stages ensure that the final product is functional, durable, and meets the required standards. Below is a simplified flowchart of the typical PCB assembly process:
PCB Assembly Flow Chart
- 1. PCB Design and Layout – The first step in PCB assembly is designing the circuit and laying out the components.
- 2. PCB Manufacturing – After the design is finalized, the PCB is manufactured, which includes etching copper traces on the board.
- 3. Solder Paste Printing – A thin layer of solder paste is applied to the PCB, preparing it for component placement.
- 4. Component Placement – Automated machines place components onto the PCB based on the design layout.
- 5. Reflow Soldering – The assembled PCB goes through a reflow oven where the solder paste melts, creating strong connections.
- 6. Inspection and Testing – The PCB is tested for functionality and inspected for defects or errors.
- 7. Final Assembly – The final step includes adding additional components or housing, preparing the product for shipment.
Stages of the PCB Assembly Process
The PCB assembly process consists of several key stages, each of which plays a vital role in ensuring that the assembly meets high standards of quality and functionality. Let’s dive deeper into these stages:
1. PCB Design and Layout
PCB design is the first and most crucial step in the process. Engineers use specialized software tools to create the layout of the circuit. This layout determines the positioning of components, routing of traces, and electrical connections. A high-quality design is essential for creating a functional and reliable PCB.
2. PCB Manufacturing
Once the design is complete, the PCB is manufactured. The manufacturing process involves the creation of the actual PCB by printing copper traces, drilling holes, and adding layers to the board. This stage ensures that the physical structure of the PCB is in place to support the electronic components.
3. Solder Paste Printing
Solder paste is applied to the PCB using a stencil printing method. This paste is essential for creating strong electrical connections between the components and the PCB. It is important that the solder paste is applied uniformly to avoid defects during the soldering process.
4. Component Placement
In this stage, the components are placed onto the PCB. This is usually done using automated pick-and-place machines, which are highly accurate. The components are placed exactly where they are needed according to the design layout, ensuring proper alignment for the next stage of the process.
5. Reflow Soldering
The PCB, with the placed components, is passed through a reflow oven, where heat is applied to melt the solder paste. The molten solder creates the necessary electrical connections between the components and the PCB. After the solder cools, it solidifies, securing the components in place.
6. Inspection and Testing
At this stage, the PCB is subjected to rigorous testing and inspection to ensure that all components are correctly placed and soldered. Automated optical inspection (AOI) and X-ray inspection are commonly used methods to detect issues such as soldering defects, misalignments, and missing components. Additionally, functional testing is carried out to check the overall performance of the PCB.
7. Final Assembly
Once the PCB passes inspection and testing, the final assembly process begins. Additional components or enclosures may be added to the PCB, depending on the final product requirements. The fully assembled product is then ready for shipment to customers or for integration into a larger system.
Role of Wintech in PCB Assembly

Wintech is a leading provider of turnkey PCB assembly services, specializing in high-mix, low-to-mid volume electronics manufacturing. With a proven track record of delivering customized and state-of-the-art solutions, Wintech is well-equipped to handle complex PCB assembly needs. They offer:
- High-Precision PCB Layout: Wintech specializes in high-level, complex, and large-size PCB layouts that require high precision.
- PCB Assembly & PCBA SMT: The company provides comprehensive PCB assembly services, including Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) for efficient assembly.
- Quick Turnaround PCB Prototypes: Wintech offers fast PCB prototype assembly to help companies test their designs and bring new products to market quickly.
- New Product Introduction (NPI): Wintech assists in the NPI process, helping clients transition from design to mass production seamlessly.
- Plastic Molding & Metal Precision Machining: In addition to PCB assembly, Wintech also offers services like plastic molding and metal machining, ensuring comprehensive product solutions.
Key Benefits of PCB Assembly
Investing in high-quality PCB assembly offers numerous benefits to electronics manufacturers, including:
- Cost-Effectiveness: High-volume production allows for reduced manufacturing costs per unit, making PCBs more affordable.
- Improved Quality: The use of automated equipment and rigorous testing ensures that the PCBs meet high standards of reliability and performance.
- Flexibility: Manufacturers can produce a wide range of PCB designs and configurations, accommodating various customer needs.
- Fast Production Time: Automated systems speed up the manufacturing process, enabling quick turnaround times for customers.
Conclusion
The PCB assembly manufacturing process is a multi-step procedure that ensures the creation of reliable and functional electronic products. Companies like Wintech provide end-to-end PCB assembly solutions, offering high-quality services tailored to meet customer specifications. Whether for high-mix, low-volume production or large-scale manufacturing, understanding the PCB assembly flow is crucial for any business involved in electronics production.
Summary Table
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| PCB Design and Layout | The initial stage where the PCB layout is created using specialized software tools. |
| PCB Manufacturing | The physical creation of the PCB, including copper etching and drilling. |
| Solder Paste Printing | A thin layer of solder paste is applied to the PCB for component placement. |
| Component Placement | Automated machines place components onto the PCB according to the layout. |
| Reflow Soldering | The solder paste is melted to form permanent electrical connections. |
| Inspection and Testing | Inspection and testing to ensure the assembly functions correctly. |
| Final Assembly | Any additional components are added to the PCB before it’s ready for shipment. |