Difference Between CCA and PCBA: Understanding Key Concepts in Electronics Manufacturing
Table of Contents
Introduction to Difference Between CCA and PCBA
In the field of electronics manufacturing, terms like CCA (Circuit Card Assembly) and PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) are often used interchangeably. However, while they share similarities, there are important distinctions between them.
Understanding the difference between CCA and PCBA is crucial for engineers, OEMs, and companies sourcing electronic manufacturing services. In this guide, we’ll break down their definitions, processes, and applications — and introduce how Wintech, a global leader in electronics manufacturing, delivers superior solutions for both.
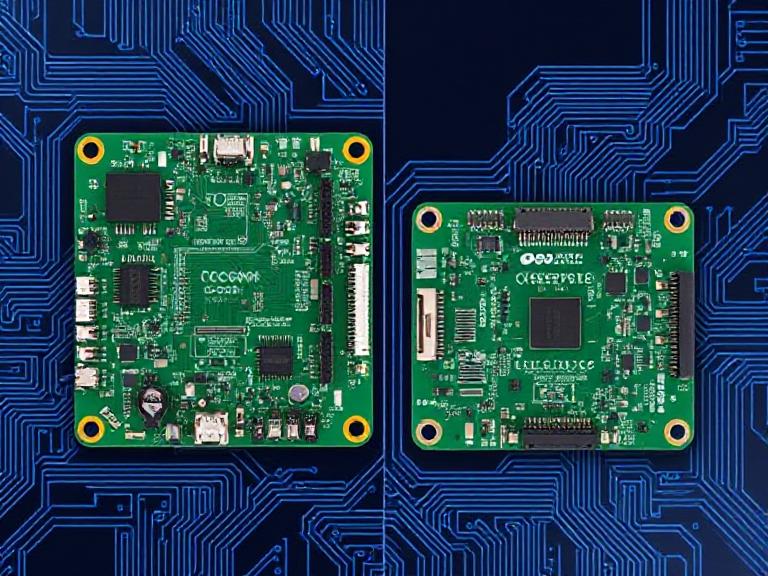
What Are CCA and PCBA?
What is PCBA?
A Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) refers to a complete board that includes the bare PCB populated with electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, ICs, and connectors through SMT (Surface Mount Technology) or THT (Through-Hole Technology).
- PCBA = PCB + electronic components + soldering process.
- PCBA is the fully functional electronic board ready to integrate into larger systems.
- Used in consumer electronics, medical devices, aerospace, and industrial applications.
What is CCA?
A Circuit Card Assembly (CCA) is similar to a PCBA but often refers to assemblies used in military, aerospace, and industrial systems. The term “card” emphasizes that the board is part of a more complex system and meets stricter standards such as IPC Class 3 or military-grade compliance.
- CCA = PCB + components + high-level testing and military/aerospace standards.
- Focuses more on ruggedization, reliability, and traceability.
- Includes advanced inspection methods such as X-ray testing and functional verification.
Key Differences Between CCA and PCBA
While both CCAs and PCBAs are assemblies of circuit boards, they differ in terminology, application, quality requirements, and testing processes. Below is a detailed comparison:
| Aspect | CCA (Circuit Card Assembly) | PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High-reliability assembly used in aerospace, defense, and industrial systems. | General-purpose electronic assembly used in consumer and commercial products. |
| Industry Standard | Complies with IPC Class 3 / MIL-SPEC | Complies with IPC Class 1 or 2 |
| Testing | Extensive functional testing, environmental screening, and traceability | Basic electrical testing and visual inspection |
| Reliability Level | Very high (mission-critical applications) | Moderate to high (commercial applications) |
| Cost | Higher due to stringent standards and inspections | Lower due to mass production and less complexity |
The Manufacturing Process: From PCB to PCBA and CCA
The process of turning a bare PCB into a fully assembled PCBA or CCA involves multiple precision-driven steps. Let’s look at the typical process flow.
1. PCB Design and Layout
The journey begins with PCB design and layout. Engineers create schematics, routing, and layer configurations based on functionality and electrical requirements. Companies like Wintech offer high-level, complex PCB layout solutions for demanding applications.
2. PCB Manufacturing
Once the layout is finalized, the PCB is fabricated using FR4, aluminum, or high-frequency materials. Layers are laminated, drilled, and plated to create conductive pathways.
3. Component Procurement
For both PCBA and CCA, reliable sourcing of components is critical. CCA sourcing typically requires traceable, certified components to meet defense or aerospace standards.
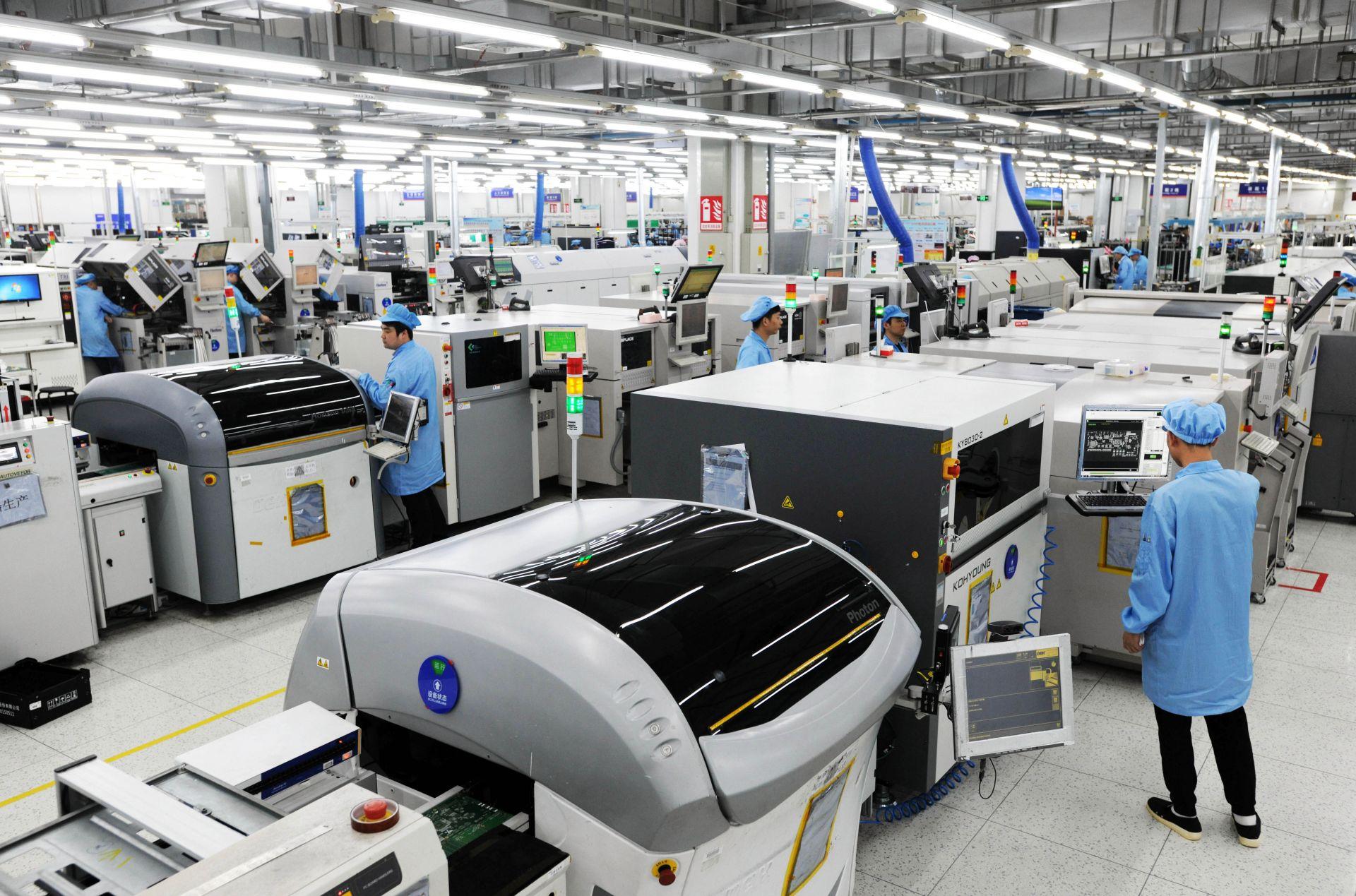
4. Component Assembly (SMT & THT)
Using advanced pick-and-place machines, components are mounted onto the PCB. In high-reliability CCAs, manual soldering and inspection may complement automation.
5. Inspection and Quality Control
Inspection ensures flawless assembly. Typical methods include:
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
- X-Ray Inspection
- In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
- Functional and Burn-in Testing (especially for CCAs)
6. Conformal Coating and Encapsulation
CCAs often receive additional protection such as conformal coating to resist humidity, dust, and vibration — essential in aerospace and military environments.
7. Final Integration and System Testing
The final stage ensures the assembly meets design intent and performance standards before delivery.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
Knowing the distinction between CCA and PCBA helps businesses make informed sourcing and design decisions. For instance:
- OEMs in aerospace and defense should specify CCA to ensure reliability.
- Consumer electronics brands can choose PCBA for cost-effective, high-volume production.
- R&D teams can plan testing requirements and certifications early in the design stage.
About Wintech – Your Trusted Partner in Electronics Manufacturing

Wintech is a full turnkey service provider specializing in high-mix, low to mid-volume electronics manufacturing and custom material solutions. With a proven track record of delivering state-of-the-art solutions, Wintech has earned the trust of many Fortune 500 companies worldwide.
Our Core Services
- PCB Design & Layout: High-precision designs for complex systems.
- PCB Manufacturing: Multi-layer and HDI PCBs for demanding applications.
- PCB Assembly & PCBA SMT: Advanced SMT lines for prototype to mass production.
- Quick Turn PCB Prototyping: Rapid turnaround for R&D and NPI projects.
- Plastic Molding & Metal Machining: Custom enclosures, chassis, and mechanical integration.
- Cable Harness & Assembly: Complete system interconnect solutions.
With advanced manufacturing capabilities, Wintech specializes in high-precision, large-size, and complex structure assemblies. Their integrated system ensures quality consistency, cost control, and faster time-to-market for customers worldwide.
Summary Table
| Aspect | CCA | PCBA |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Aerospace, Defense, Industrial | Consumer, Commercial, Automotive |
| Quality Standard | IPC Class 3 / MIL-SPEC | IPC Class 1 / 2 |
| Testing Level | Advanced Functional and Environmental Tests | Standard Electrical and Visual Tests |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Durability | Extremely High | Moderate to High |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is a CCA the same as a PCBA?
No. While both refer to circuit assemblies, CCAs are designed for higher reliability and often used in aerospace or defense, whereas PCBAs are for general electronics.
2. What materials are used in CCAs and PCBAs?
They are built on FR4, aluminum, or polyimide PCBs, with components like ICs, resistors, and capacitors assembled using SMT or THT methods.
3. How does Wintech ensure quality in PCBA production?
Wintech uses advanced CNC automation, vacuum reflow, AOI, X-ray inspection, and ISO-certified processes to guarantee quality and reliability.
4. What industries use CCAs?
Defense, aerospace, industrial automation, and medical equipment manufacturers commonly require CCAs for mission-critical reliability.
5. Can Wintech handle both PCBA and CCA projects?
Yes. Wintech provides full turnkey solutions for both PCBA and CCA manufacturing — from prototyping to large-scale production.