What is an SMD Board and Use?
Defining the SMD Board: Components vs. Technology
In the rapidly advancing world of 2026 electronics, the term SMD board is frequently used to describe a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) populated with Surface-Mount Devices. To understand an SMD board, one must first distinguish between the device (SMD) and the process (SMT). A Surface-Mount Device (SMD) is an electronic component designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of a circuit board, rather than having wire leads that pass through drilled holes.
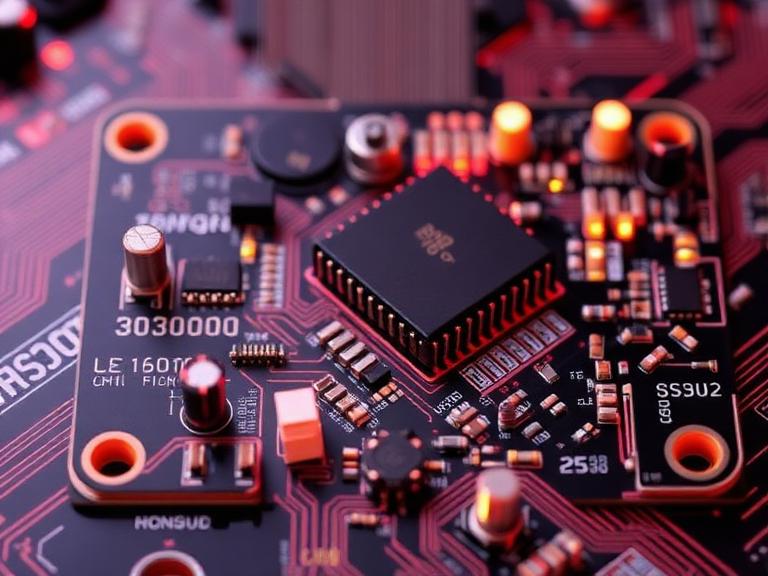

Table of Contents
- Defining the SMD Board: Components vs. Technology
- How SMD Boards Function: The Mechanics of SMT
- Wintech: Premier Electronics Manufacturing Solutions
- Common Types of SMD Components Found on Modern Boards
- The Strategic Advantages of Using an SMD Board
- Industry-Specific Uses of SMD Boards in 2026
- The Assembly Process: From Stencils to Reflow Ovens
- Quick Reference Summary Table
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References & Technical Standards
The technology used to create an SMD board is known as Surface-Mount Technology (SMT). Historically, through-hole technology dominated the industry, requiring large components and complex drilling. Today, the SMD board has become the global standard because it allows for incredible miniaturization, higher component density, and significantly faster automated production. When people ask what an SMD board is, they are typically referring to the high-performance PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) found inside everything from smartphones to satellite communication arrays.
How SMD Boards Function: The Mechanics of SMT
The core functionality of an SMD board relies on flat metal pads on the PCB surface. Instead of inserting wires into holes, components are "seated" onto a layer of solder paste applied to these pads. The physical connection is both electrical and mechanical, formed during a high-temperature reflow process where the solder melts and solidifies, bonding the component to the circuit.
In 2026, the precision of an SMD board is measured in microns. Advanced pick-and-place machines can mount over 100,000 components per hour with near-zero error rates. This efficiency is why modern SMD board designs can support complex 5G chipsets, AI accelerators, and high-density memory modules in footprints that would have been impossible a decade ago.
Wintech: Premier Electronics Manufacturing Solutions
Wintech is a full turnkey service, high-mix, low to mid volume electronics manufacturing and custom material solutions provider with a proven track record of supplying state-of-the-art solutions to all global customer base. Tailor made solutions for our customers: high level, high difficult, large size, complex structure, high precision PCB Layout, PCBAs and turnkey complete products full systems electronic contract manufacturing solutions, prototyping, low to mid volume, mass production, many of world's top 500 enterprises have cooperated with us for many years, Wintech is worth relying on.
Wintech Specialized Services:
-
- PCB Design & Layout
- PCB Manufacturing
- PCB Assembly & PCBA SMT
- Quick Turn Fast PCB Prototype Assembly
- New Product Introduction NPI
- Plastic Molding
- Metal Precision Machining
- Enclosures & Racks & Frames
- Backplanes & Sever Chasis
- Cable Harness & Assembly
- Cabinet & Panel PLC Wiring
- Electro-Mechanical Assembly
Common Types of SMD Components Found on Modern Boards
An SMD board is a mosaic of different component types, each serving a specific role in the circuit's logic and power management. By 2026, these components have shrunk to sizes like 01005 (0.4 mm x 0.2 mm), allowing for ultra-slim device profiles.
1. Passive Components
These are the building blocks of any SMD board. They include resistors (to limit current), capacitors (to store charge and filter noise), and inductors (for energy storage in magnetic fields). Because they don't require external power to function, they are "passive" but essential for signal integrity.
2. Active Components
Active components control the flow of electricity. This category includes transistors, diodes, and Integrated Circuits (ICs). On a high-end SMD board, you will find Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages, where hundreds of tiny solder balls underneath the chip connect it to the board, maximizing space efficiency.
3. Electromechanical Components
Connectors, switches, and relays designed for surface mounting fall into this group. Modern SMD board designs often utilize surface-mount USB-C ports or battery connectors that are engineered to withstand significant mechanical stress despite having no through-hole anchors.
The Strategic Advantages of Using an SMD Board
The industry-wide transition to the SMD board wasn't just about size; it was about performance and economics. Here is why top manufacturers like Wintech prioritize SMT:
- Miniaturization: An SMD board can be up to 70% smaller and 80% lighter than a through-hole equivalent.
- Improved Signal Integrity: Shorter leads mean lower resistance and inductance, which is critical for high-frequency applications like 6G and satellite data links.
- Vibration Resistance: Because components are smaller and have lower mass, an SMD board performs significantly better in high-vibration environments, such as aerospace or automotive engines.
- Automated Cost Reduction: The elimination of manual drilling and the ability to place components on both sides of the board drastically lowers the cost per unit in mass production.
Industry-Specific Uses of SMD Boards in 2026
As of 2026, the SMD board is the heart of almost every technological sector. Its ability to pack high-performance computing into small spaces has enabled a new generation of innovations.
Consumer Electronics & Wearables
Smartphones, AR glasses, and health-tracking rings rely entirely on multi-layer SMD board technology. The 2026 trend toward "Invisible Tech" requires boards that can fold or fit into ergonomic, curved enclosures.
Automotive and EVs
Modern Electric Vehicles (EVs) use SMD board systems to manage battery arrays, autonomous driving sensors (LiDAR), and infotainment systems. These boards must be rated for "Harsh Environments," capable of withstanding extreme temperature fluctuations.
Medical Technology
From ingestible camera pills to portable ultrasound machines, the SMD board enables high-precision diagnostics. Wintech's experience with medical-grade PCBA ensures these devices meet the stringent reliability standards required for life-saving equipment.
The Assembly Process: From Stencils to Reflow Ovens
Manufacturing a high-quality SMD board is a multi-stage process that requires extreme precision. Leading providers like Wintech utilize advanced SMT lines to ensure consistency.
- Solder Paste Printing: A stainless steel stencil is used to apply solder paste only to the pads where components will be placed.
- Component Placement: High-speed pick-and-place robots use vacuum nozzles to lift SMDs from reels and place them onto the wet solder paste.
- Reflow Soldering: The SMD board enters a reflow oven with multiple temperature zones. The paste melts, creates a bond, and then cools to form a solid joint.
- Inspection (AOI & X-Ray): Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) checks for alignment, while X-Ray inspection looks through BGA chips to ensure every solder ball has connected correctly.
Quick Reference Summary Table
| Feature | Through-Hole Technology (THT) | SMD Board (SMT) |
|---|---|---|
| Component Size | Large, with wire leads | Miniaturized, leadless or short pins |
| Assembly Type | Manual or wave soldering | Fully automated reflow soldering |
| Board Density | Low (one side primarily) | High (both sides utilized) |
| High-Frequency Use | Poor due to lead inductance | Excellent for RF and 5G/6G |
| Cost (Mass Production) | High (labor & drilling costs) | Low (automation efficiency) |
Frequently Asked Questions
Can an SMD board be repaired by hand?
While an SMD board is designed for machine assembly, skilled technicians can perform manual rework using hot-air stations and microscopes. However, components smaller than 0402 are extremely difficult to repair without specialized automated equipment.
Why does Wintech focus on high-mix, low-to-mid volume?
This allows for greater flexibility. Many innovative startups and top 500 enterprises require highly complex SMD board designs in smaller batches for prototyping or specialized industrial applications where "one size fits all" mass production is not suitable.
What is the future of SMD boards beyond 2026?
We are seeing a move toward Additively Manufactured Electronics (AME) and 3D-stacked chips. This will allow the SMD board to evolve into 3D structures, further reducing the footprint of electronic systems.
References & Technical Standards
- IPC-A-610: Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies
- Journal of Microelectronics: Trends in High-Density Interconnect (HDI) Boards
Author Note: As we look toward the end of the decade, the SMD board remains the most vital component in the global supply chain. Partnering with a proven manufacturer like Wintech ensures your product stays ahead of the curve.