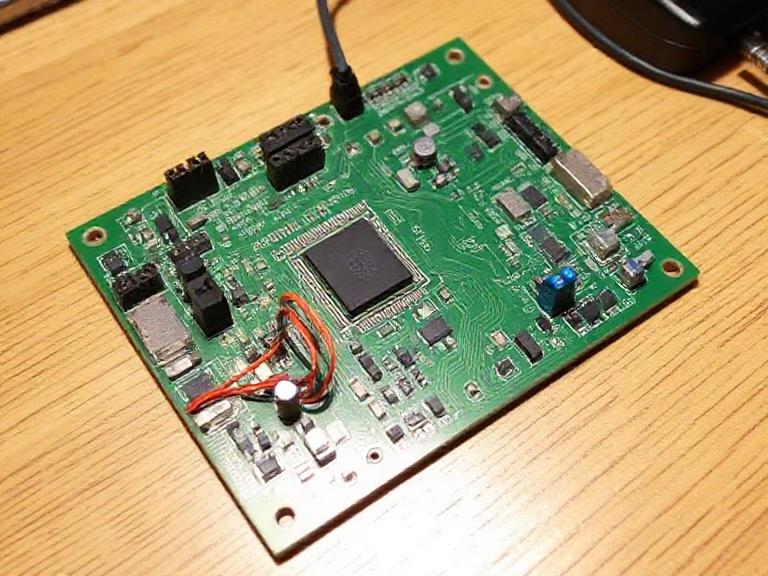
How Is a Circuit Board Assembled? Full Guide to PCB Manufacturing & Assembly
Understanding how a circuit board assembled process works is essential for engineers, product developers, and businesses that rely on electronic devices. This comprehensive guide explains how a circuit board assembled workflow is completed from design to full box-build production, including SMT assembly, testing, quality control, and turnkey manufacturing. With rising demand for precision electronics across industries, knowing how a circuit board assembled process functions helps companies achieve efficient production, reduce defects, and accelerate time-to-market.

This article provides a step-by-step breakdown, real-world examples, a summary table, FAQ section, and an extended company spotlight on Wintech, a proven global provider of high-mix electronics manufacturing solutions.
Table of Contents
Introduction: What Does It Mean to Have a Circuit Board Assembled?
When companies refer to having a circuit board assembled, they are talking about the complete process of creating a functional electronic assembly from raw materials. This includes PCB layout, bare board fabrication, component sourcing, SMT placement, soldering, inspection, testing, and final system integration. A circuit board assembled product must meet electrical, mechanical, and reliability standards suitable for its end-use applications—from consumer products and medical devices to industrial controls and aerospace electronics.
The phrase circuit board assembled captures both the physical assembly of components and the engineering steps required for precision, quality, and compliance.
How Is a Circuit Board Assembled? (Step-by-Step Process)
To understand how a circuit board assembled workflow functions, we break the process into eight key stages.
1. PCB Design & Layout
Before a circuit board assembled project can begin, engineers must produce a complete PCB layout using ECAD software. The design ensures proper signal integrity, impedance matching, EMC compliance, power distribution, and manufacturability (DFM). High-quality layout prevents issues during component placement and soldering.
2. PCB Manufacturing (Bare Board Fabrication)
Once the design is finalized, PCB fabrication begins. This involves:
- Copper etching
- Layer lamination
- Via drilling (mechanical, laser, HDI)
- Surface finishing (ENIG, HASL, OSP, immersion silver, etc.)
- Solder mask and silkscreen application
The quality of this step significantly influences how smoothly the circuit board assembled process proceeds.
3. Component Sourcing & Material Preparation
All components required for the circuit board assembled unit must be procured, inspected, and prepared. This includes ICs, resistors, capacitors, connectors, sensors, and mechanical parts. High-mix assembly requires strict traceability and BOM accuracy.
4. SMT (Surface Mount Technology) Assembly
a. Solder Paste Printing
A stainless steel stencil is used to apply precise solder paste deposits on the pads. Correct printing is crucial for a defect-free circuit board assembled product.
b. Component Pick-and-Place
High-speed SMT machines place components at thousands of placements per minute. This ensures alignment, orientation, and consistency during the circuit board assembled stage.
c. Reflow Soldering
The PCB passes through a reflow oven, melting solder paste and forming reliable mechanical and electrical connections.
5. Through-Hole Assembly (THT)
Not all components are SMT. Some require manual or wave soldering, especially connectors, transformers, and large electrolytics. This adds strength and ensures the circuit board assembled board meets industry durability standards.
6. Inspection & Testing
A high-quality circuit board assembled process relies on strict testing, including:
- AOI (Automated Optical Inspection)
- X-ray inspection for BGA devices
- ICT (In-Circuit Testing)
- Functional testing
- Burn-in testing for reliability
Testing ensures that every circuit board assembled unit performs exactly as designed.
7. Conformal Coating & Protection
To protect the circuit board assembled PCBA from humidity, chemical exposure, dust, and corrosion, protective coatings such as acrylic, silicone, or parylene are applied.
8. Box Build & System Integration
Finally, the circuit board assembled PCBA is integrated into enclosures, racks, frames, and complete end-use devices. This stage completes the transformation from a raw circuit layout to a finished, ready-to-ship electronic product.
Summary Table: How a Circuit Board Is Assembled
| Step | Description | Role in Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| PCB Design | Electrical & mechanical layout design | Defines the base for the circuit board assembled product |
| PCB Fabrication | Copper etching, drilling, plating, finishing | Creates bare board for component mounting |
| Component Sourcing | BOM management & component purchasing | Ensures correct parts for assembly |
| SMT Assembly | Solder paste, placement, reflow | Forms core electrical connections |
| THT Assembly | Manual or wave soldering | Required for large or mechanical parts |
| Inspection | AOI, X-ray, ICT, functional tests | Guarantees quality of the circuit board assembled |
| Coating | Moisture and chemical protection | Enhances long-term reliability |
| Box Build | Final product integration | Completes the electronic device |
Company Spotlight: Wintech Electronics Manufacturing
Wintech is a global leader in high-mix, low to mid-volume electronics manufacturing, offering full turnkey solutions for customers requiring advanced circuit board assembled products. With a proven track record of working with Fortune 500 companies, Wintech delivers high-level engineering, precision manufacturing, and reliable global support.
Why Wintech Is a Trusted Manufacturing Partner
- High-difficulty, large-size, and complex PCB assemblies
- Precision engineering for mission-critical devices
- Rapid prototyping and low to mid-volume runs
- Full system integration, racks, frames, and enclosures
Wintech Core Services
- PCB Design & Layout
- PCB Manufacturing
- PCB Assembly & PCBA SMT
- Quick Turn Fast PCB Prototype Assembly
- New Product Introduction NPI
- Plastic Molding
- Metal Precision Machining
- Enclosures & Racks & Frames
For businesses needing highly engineered circuit board assembled solutions, Wintech delivers complete manufacturing—from concept to finished product.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long does it take to have a circuit board assembled?
Prototype runs can take 24 hours to a few days. Full production typically ranges from one to six weeks depending on complexity and component availability.
2. What affects the cost of having a circuit board assembled?
Key cost factors include board layer count, part density, special finishes, BGA complexity, testing requirements, and order quantity.
3. What is the difference between PCB and PCBA?
A PCB is the bare circuit board. A PCBA is a fully circuit board assembled unit with all components installed.
4. Can Wintech support low-volume production?
Yes—Wintech specializes in high-mix, low to mid-volume, and complex assemblies.